| Balsam apple - Momordica balsamina | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Fig. 1  Ripening fruits  Fig. 2  Malilangwe Wildlife Reserve, Zimbabwe  Fig. 3  Vilankulo, Inhambane, Mozambique  Fig. 7  Malilangwe Wildlife Reserve, Zimbabwe  Fig. 8  Vilankulo, Inhambane, Mozambique  Fig. 9  Habitus and leaves. M. balsamina, Cucurbitaceae, Balsam Apple, Cundeamor, Southern, Balsam Pear, riping fruits; cultivated in a private garden | Scientific
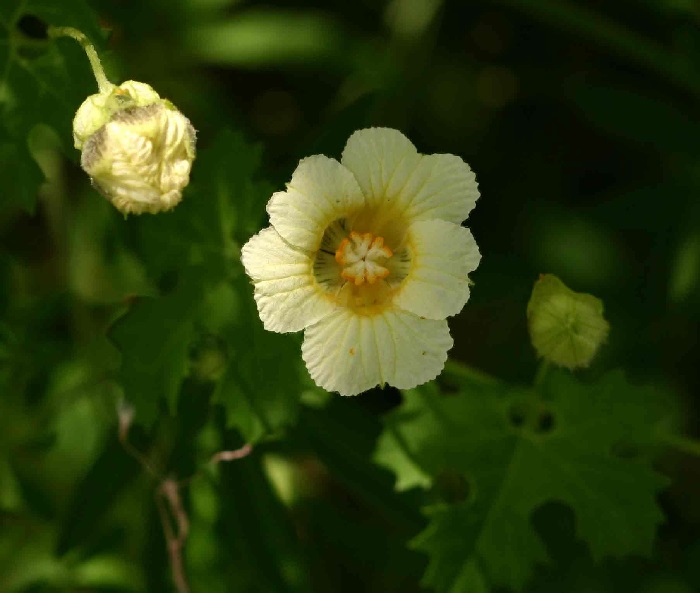
name Momordica balsamina L. Common names English: balsam-apple, southern balsampear; French: pomme de merveille; German: Balsamapfel; Portuguese: balsâmina-de-purga; Spanish: balsamina; Swedish: balsamgurka; Urdu (Pakistan): jangli karela 1,2 Synonyms M. balsamina var. huberi, M. balsamina var. leucantha, M. balsamina var. minor, M. garipensis, M. huberi, M. involucrata, M. involucrata var. laciniata, M. involucrata var. normalis, Nevrosperma cuspidatum 3 Relatives Bitter melon, M. charantia L.; spiny gourd, M. cochinchinensis (Lour.) Spreng. Family Cucurbitaceae Origin Africa, Asia; Arabian Peninsula, Indian Subcontinent; Australasia USDA hardiness zones 8-10 2 Uses Fruits: pickled, cooked vegetable; young shoots and tendrils: boiled; medicines Life form Perennial tendril-bearing climber Height/spread Prostrate or scandent stems up to 9 ft (2.7 m) long 5 Plant habit Climbing or smothering growth habit 2 Leaves 3.5-5 in. (9-12 cm), broadly ovate, deeply 5-7 lobed 5 Flowers Unisexual on the same plant, pale yellow, cream or white Fruit Egg shaped, 3 in. (8 cm) long 6 Invasive potential * Not considered a problem species at this time Known hazard Poisonous to mammals 1 Reading Material Momordica - Momordica spp., University of Florida pdf Bitter Gourd, Balsam Pear: Pharmacy On A Fence, Eattheweeds.com Bittermelon. Cucurbit Production Chapter, Vegetable Production Handbook of Florida, University of Florida pdf Origin A native of Zimbabwe 5 Description Perennial climber with prostrate or scandent stems up to 2.7 m long. Tendrils simple. Leaves up to 9 × 12 cm, broadly ovate to almost circular in outline, deeply 5-7 lobed, each lobed often 3-5 lobed again, deeply cordate at the base; ultimate margin with sinuate teeth. Found in woodland, wooded grassland and riverine fringes, often on sandy soils. 5 Flowers
Fig. 4. Flower, M. balsamina, Cucurbitaceae, Balsam Apple, Cundeamor, Southern, Balsam Pear, riping fruits; cultivated in a private garden Fig. 5. Malilangwe Wildlife Reserve, Zimbabwe Fig. 6. Inhaca Island, Mozambique Fruit Fruit ovoid, tuberculate, beaked, 2.5 - 6.5 cm long orange-red to red when ripe. 5
Fig. 10. Developing fruit, M. balsamina, cucurbitaceae, balsam Apple, cundeamor, southern, balsam pear, riping fruits; cultivated in a private garden. Fig. 11. Ripe fruit Fig. 12. Fruit, beginning of splitting open Fig. 13. Fruit, splitting open Fig. 14. Fruit with seeds Food Uses The fruit can be pickled or after soaking used as a cooked vegetable. Young shoots and tendrils are boiled as a green. The seeds are eaten in cooked young fruit. 4 The fruit, 3-inch long, orange-colored, egg-shaped fruit is used in a similar manner to bitter melon - M. charantia L. 6 Other Edibles in the Momordica genus: Bitter Melon, M. charantia Gac, Chinese cucumber, M. cochinchinensis General
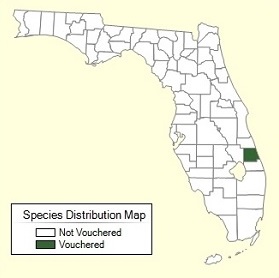
Fig 15. Florida Distribution Map of M. balsamina M. balsamina, which has longer spines on the fruit (than M. charantia) and can ripen to red, grows only in St. Lucie County in Florida and only a smattering of places in the southern U.S. 4 Further Reading Bitter Gourd: Botany, Horticulture, Breeding, Horticultural Reviews pdf Balsam Apple, 1919, Sturtevant’s Edible Plants Of The World Balsam Apple Botanical Art List of Growers and Vendors | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bibliography 1 "Taxon: "Momordica balsamina L." No. 24519. 28 May 2009. U.S. National Plant Germplasm System, www.ars-grin.gov/npgs/. Accessed 14 Jan. 2018. 2 "Momordica balsamina." 2007, 2017. Assessment of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas, assessment.ifas.ufl.edu/assessments/momordica-balsamina/. Accessed 14 Jan. 2018. 3 Wunderlin, R. P., B. F. Hansen, A. R. Franck, and F. B. Essig. "Momordica balsamina L." 2018. Atlas of Florida Plants. [S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), USF Water Institute.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa. florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Plant.aspx?id=1746. Accessed 27 Jan. 2018. 4 Deane, Green. "Bitter Gourd, Balsam Pear: Pharmacy On A Fence." Eat The Weeds and other things, too. www.eattheweeds.com/bitter-gourd-balsam-pear-pharmacy-on-a-fence/. Accessed 14 Jan. 2018. 5 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018). "Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: Momordica balsamina." www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/species.php?species_id=157160. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. 6 Stephens, James M. "Momordica, Momordica spp." This document is HS627, one of a series of the Horticultural Sciences Department, UF/IFAS Extension. Original publication date May 1994. Revised September 2015, edis.ifas.ufl.edu/mv094. Accessed 1 July 2017. Photographs Fig. 1 Zell, H. Riping fruits. 29 July 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_004.JPG. Accessed 13 Jan.2018. Fig. 2 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=3. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 3 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=11. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 4 Zell H. Flower. M. balsamina, Cucurbitaceae, Balsam Apple, Cundeamor, Southern, Balsam Pear, riping fruits; cultivated in a private garden. Assessment of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas, 3 July 2011, (CC BY-SA 3.0), assessment.ifas.ufl.edu/assessments/momordica-balsamina/. Accessed 8 Jan. 2018. Fig. 5 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: : Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=2. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 6 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=14. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 7 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=1. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 8 Hyde, M.A., Wursten, B.T., Ballings, P. & Coates Palgrave, M. (2018), Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: individual images: Momordica balsamina, www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/image-display.php?species_id=157160&image_id=8. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018. Fig. 9 Zell H. Habitus and leaves. 8 July 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_001.JPG#mediaviewer/File:Momordica_balsamina_001.JPG. Accessed 8 Jan. 2018. Fig. 10 Zell, H. Developping fruit. 16 July 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG Accessed 13 Jan. 2018. Fig. 11 Zell, H. Ripe fruit. 29 July 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_005.JPG. Accessed 13 Jan. 2018. Fig. 12 Zell, H. Fruit, beginning of splitting open. 12 Aug. 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_006.JPG. Accessed 13 Jan. 2018. Fig. 13 Zell, H. Fruit, splitting open. 12 Aug. 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_007.JPG. Accessed 13 Jan. 2018. Fig. 14 Zell, H. Fruit with seeds. 12 Aug. 2009, (CC BY-SA 3.0), commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Momordica_balsamina_003.JPG#/media/File:Momordica_balsamina_008.JPG. Accessed 13 Jan. 2018. Fig. 15 Wunderlin, R. P., B. F. Hansen, A. R. Franck, and F. B. Essig. "Momordica balsamina." 2018. Atlas of Florida Plants (florida.plantatlas.usf.edu).[S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), USF Water Institute.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa. Accessed 14 Jan.2018. * UF/IFAS Assessment of Non-native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas ** The information provided above is not intended to be used as a guide for treatment of medical conditions using plants. Published 28 Jan. 2018 KJ. Last update 23 Dec. 2023 LR | |||||||||||||||||||